
Современные технологии и автоматизация в машиностроении
195
properties of the processed materials. When rigorously present particles bounds inside material break be-
cause the processed workpieces are separated into components with chippings. Basic characteristics of the
cutting process depend on a number of the following factors [5]:
1) the banks specifications: the sort of material, its physical and mechanical properties, the binder
elements, etc.;
2) the tool specifications: angular parameters, physical and mechanical properties of the cutter mate-
rial, the degree of the surface roughness, edge sharpness, and so on;
3) the processing modes and dimensions: thickness and width of the layer, the feed and cutting,
speed thickness machining allowance, the cutting direction with respect to the preset direction of fibers, and
so on.
Table 1
The applied methods of composite materials processing
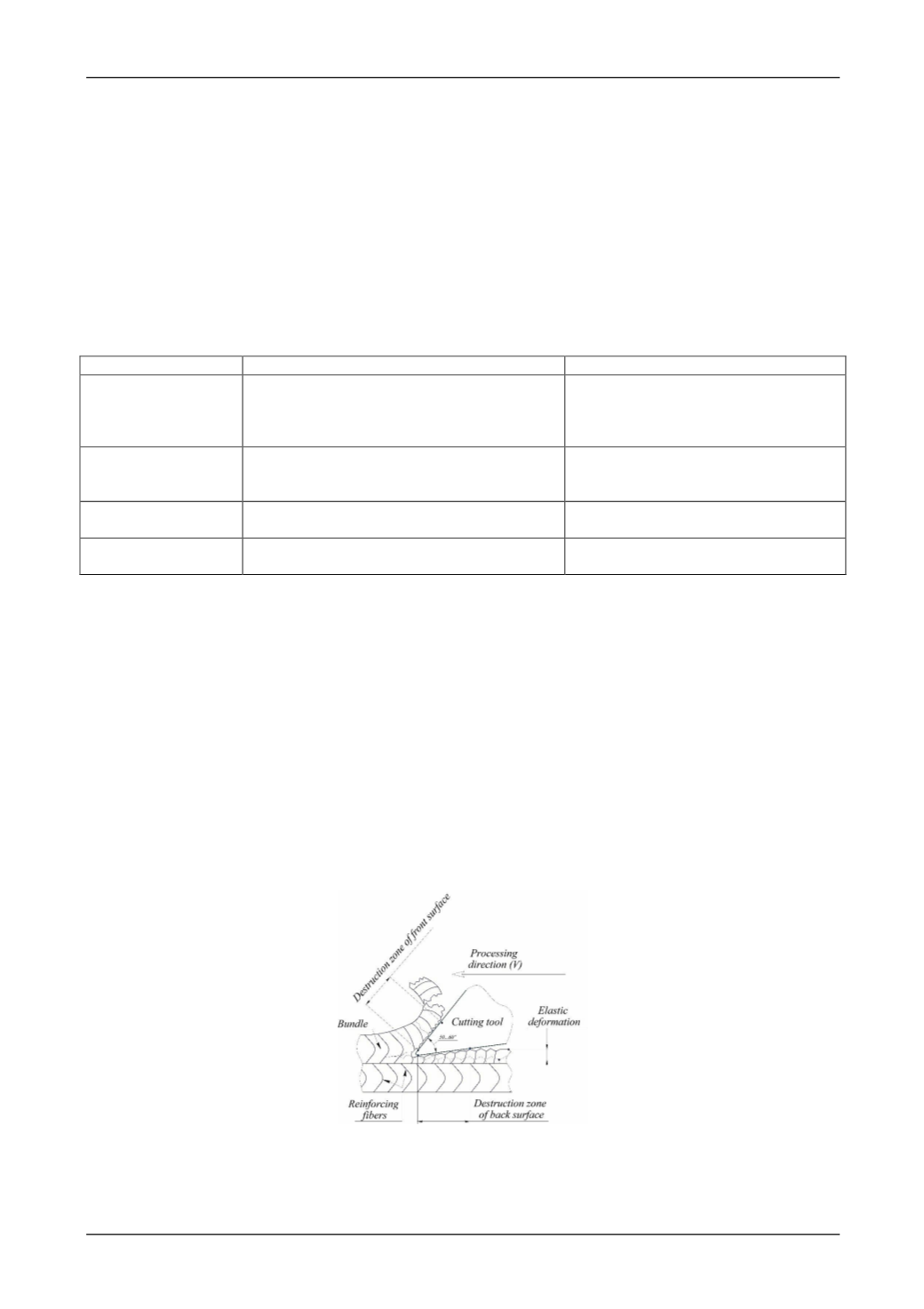
Analysis of the work of the authors [7 – 10] revealed some features of the composite materials cut-
ting. As a rule, during the composites processing wear phenomenon occurs on the back surface of the tool
due to the elastic material recovery after the cutting wedge remove (Fig.1). The tool front surface wear is
slight and results from abrasive wear of the workpiece material, and the chip friction on the front surface and
significant heat in the cutting zone. The comfortable condition for composites cutting is when the tool edge
is sharp enough to prevent any the tool- workpiece friction. The tool wear should also be minimized, since
any change of the cutting blade geometry result in an instant temperature jump in the cutting zone and
influences on its critical wear. The geometry of the tool should be selected to provide efficient process apply-
ing the minimal cutting force [6 – 12].
Recommended geometrical parameters of the cutting tool intended for composites processing are
specified by the following range of requirements: front corner: γ = 20... 30°, clearance angle α = 10...15°,
sharpening angle β = 50...60° [8, 13].
The above given parameters are designed taking into account the conditions and requirements for the
technological processing of the manufactured articles. They define the cutting process and cutting force de-
gree, chip forming process, and the surface quality obtained after machining [5].
Fig.1. Wear mechanism of cutter surfaces when composite materials processing.
The processing features of the composite materials show that under continuous development of de-
tails manufacturing technology of composites, and there is the need in developing specialized tools taking
Тype of processing
Advantages
Disadvantages
Mechanical
Low roughness degree, high of machined
surface accuracy
High tool wear and its effect on the
processing quality, separation, tearing
fibers, the likelihood of thermal
degradation of the matrix
Jet - abrasive
Deficiency of thermal degradation of the matrix,
the large thickness processing, high level
performance
High surface roughness, the danger of
swelling in water
Laser
Small cut’s width, high speed cutting,
processing fragile detail
Thermal the destruction of the matrix,
smoke and dust formation
Ultrasonic
High machining accuracy, low surface
roughness, minimal material separation
Low productivity, tool wear














